Lots of conversations in my life these days are inspired by single tweets. And those tweets, for me at least, are often inspired by my own frustration in the media’s ineptitude on certain issues. One of those issues, of course, is understanding the effects of social media and the Internet more generally in the Arab world. The other day, after reading a jumble of cyberutopian bullshit (and yes, the real outlier stuff Evgeny Morozov talks about), I tweeted:
Please, spare me the “Internet/free flow of info/Libya” meme. 5% Internet penetration, friends, does not a “net revolution” make.
Allow me to explain. Regardless of which side of the contrived fence you stand on, you are unlikely to deny the anecdotal usage of Facebook, Twitter, and other social networking sites for political organizing in Tunisia, Egypt and elsewhere. Perhaps you, like Morozov, contend that the Internet is more a tool of repression than one of liberation.
Or perhaps you argue that these revolts would have happened without the invention of the Internet. Whatever your orientation, you are no doubt able to see how, in a country where nearly one-third of the population accesses the Internet and millions are on Facebook alone, the advent of social media was helpful in both organizing and disseminating information.
Which brings me to Libya. Libya is not, in any sense, Egypt, nor is it Tunisia. There are others who could explain the political differences, so allow me to ruminate on two interesting and very relevant factors: Internet and mobile penetration. The stats below are from the International Telecommunications Union – one of several organizations that track such data–but are generally representative:
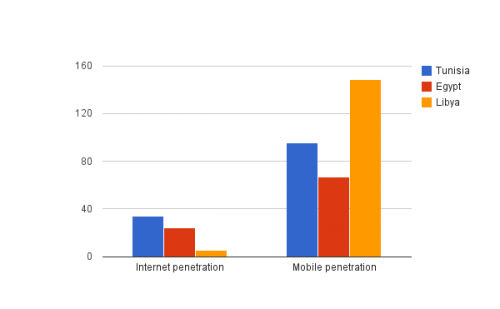
The normative question in relation to the Internet (mobile is obviously a different story) is, then, how much do basic indicators like Internet and mobile penetration affect the effectiveness of such tools for organizational or revolutionary purposes? Or, can a tiny group of Internet users* influence a countrywide movement?
After posting my tweet, I got an email of polite disagreement from Clay Shirky who, among other things, noted:
“Making the question “net revolution or nothing” kills the part of the conversation that could be about how serious the effect of the net was, in any situation. There’s a lot of space between inert and essential.”
And he’s right, of course, but I pointed out that he was not my target demographic; rather, the tweet was directed toward that elusive class of cyberutopians Morozov so often addresses (note: they might not be the majority, but they do exist). Nevertheless, it sparked an interesting conversation on various aspects of the debate, a couple of which I’ll point to here.
First up, the media. The mainstream US media has perhaps been the biggest cyberutopian of them all. I watched as, during the Tunisian revolt, they shied from overhyping the Internet then, turning to Egypt, began to gain confidence in their reporting. I fielded literally hundreds of calls from journalists who wanted to know (and I quote) “exactly how Egyptians are using social media.”
I wrote a blog post about it. I cheered a little inside that they were asking me (and more importantly, actual Egyptian activists) rather than the likes of Tom Friedman. And I did my best to talk to Egyptians and check all of my facts (which is not to say I’m always right, or right to all), as did a lot of journalists I spoke with. Bravo, all around.
And now, with Libya, we’re back to where we were in 2009 with Iran: Completely dumbfounded and, unable to check facts with Libyans on the ground, reporting inanities. Take Isabel Kershner’s garbage New York Times piece on how Arabs are surprised (gasp!) that an Israeli created an autotuned version of Qaddafi that is (gasp!) actually kind of funny. Or ABC News’s piece (parroted later by Wired) on the use of a Muslim dating site (which they claim is the “Muslim Match.com”) to “rally the revolution”.
The first example is straight up ridiculous, while the second could be true (as Shirky points out, “it is often better to think of dissidence than dissidents, because when a population gets radicalized, they will use the tools they have to hand.”) But it is nevertheless a single anecdote, not a diagnosis of how the Internet has been used in Libya.
Now, to that point: Frankly, we–and by we I mean folks in this space as well as the media–simply don’t know that much about the Libyan Internet. We know that the blogosphere is limited in size, and that the Libyan exile community is active in this space and read by Libyans in-country. We know that Internet cafes in Libya are under heavy surveillance much of the time. We know that the Internet is only nominally filtered.
We also can assume that Libyan Internet users are largely urban, a point that Shirky argues has a more complex meaning than what I had initially thought:
I think social media (net/mobile phones/digital Al Jazeera) was useful in Libya, even given 5% penetration, because of the disproportionate value net access has in what became the sites and among who became the participants of the uprising, and I don’t think this makes me a woolly headed “X Revolution” labeler — I think it makes me someone who lived through the progress from <1% penetration to ~75% in my own country, and I remember how much of an effect 5% can have on synchronization and coordination of key urban groups.
To that point, I responded that Madagascar might be an appropriate comparison to Libya in terms of Internet use for protest. Shirky agreed:
Yeah, and that’s because Antananarivo is to Madagascar more like Seoul is to South Korea than to the Cairo::Egypt — what happens in Tana is largely what happens in Madagascar, full stop, at least politically, so the leverage of small degrees of connection is hugely amplified by civic density.
I’m not feeling conclusive about any of this, but I think one of the most important points to consider in all of this is Shirky’s offhand definition of “social media” (net/mobile phones/digital Al Jazeera), to which I would add “satellite TV” and possibly landlines. Of course, acknowledging such a broad definition would challenge the media narrative as well as numerous funding initiatives.
And now to the point of mobile, which is well outside my area of expertise (and thus I invite you mobile advocates to jump in here): Libya was the first African country to reach 100% mobile penetration. It now stands at 150% (which yes, means people own more than one mobile, not uncommon in the Maghreb). Why is this playing second fiddle to the media narrative of soccer and dating sites? Why isn’t mobile the point of focus here? Hell, I ought to ask myself the same question (answer: I’m already spread too thin).
It seems obvious to me that mobile (150% penetration), and not the Web (5%) is the real champion tool here. So how do we start that conversation? What are the key factors? How do we measure one against the other? Let’s talk about that, please.
*in Libya, about 320K people have access, and we have to assume that some are apolitical or support Qaddafi
This article originally appeared here and is licensed under Creative Commons AT-NC-ND
Jillian York is a Boston-based writer, researcher, and activist. You can visit her blog, or follow her on twitter



















Comments (0)